For another 5 billion years, the Sun will provide us with energy. Current technology allows us to capture this energy and convert it into electricity or heat. So, we can cover consumption for housing and industry without carbon emissions.
Although the potential is theoretically infinite, in practice, solar energy production is faced with factors such as variability triggered by day-night sequences, but also by periods of cloudiness or very high temperatures, when overheating of the panels leads to a drop in actual production. Other factors that slow down production development are high storage costs and undersized electricity grids.
Solar energy production offers our country several important benefits:
-
- Solar energy contributes, along with other forms of renewable energy such as hydropower, wind energy, geothermal Romania's climate goals.
- It supports environmental protection through zero carbon dioxide emissions.
- It represents an economic opportunity for the production of zero emission fuels such as green hydrogen.
- It leads to new jobs. One point to note is that the development of renewable energy, including solar energy, can lead to the retraining of employees in areas that will be increasingly constrained, such as the coal industry.
1. How is solar energy produced?
There is 3 main ways for harnessing solar energy: through photovoltaic panels, solar heating and cooling systems and concentrated solar power.
Photovoltaic (PV) panels use electronic devices, called solar cells, to convert solar energy directly into electricity. Photovoltaic panels are one of the fastest growing renewable energy technologies and are playing an increasingly important role in the global energy transformation.
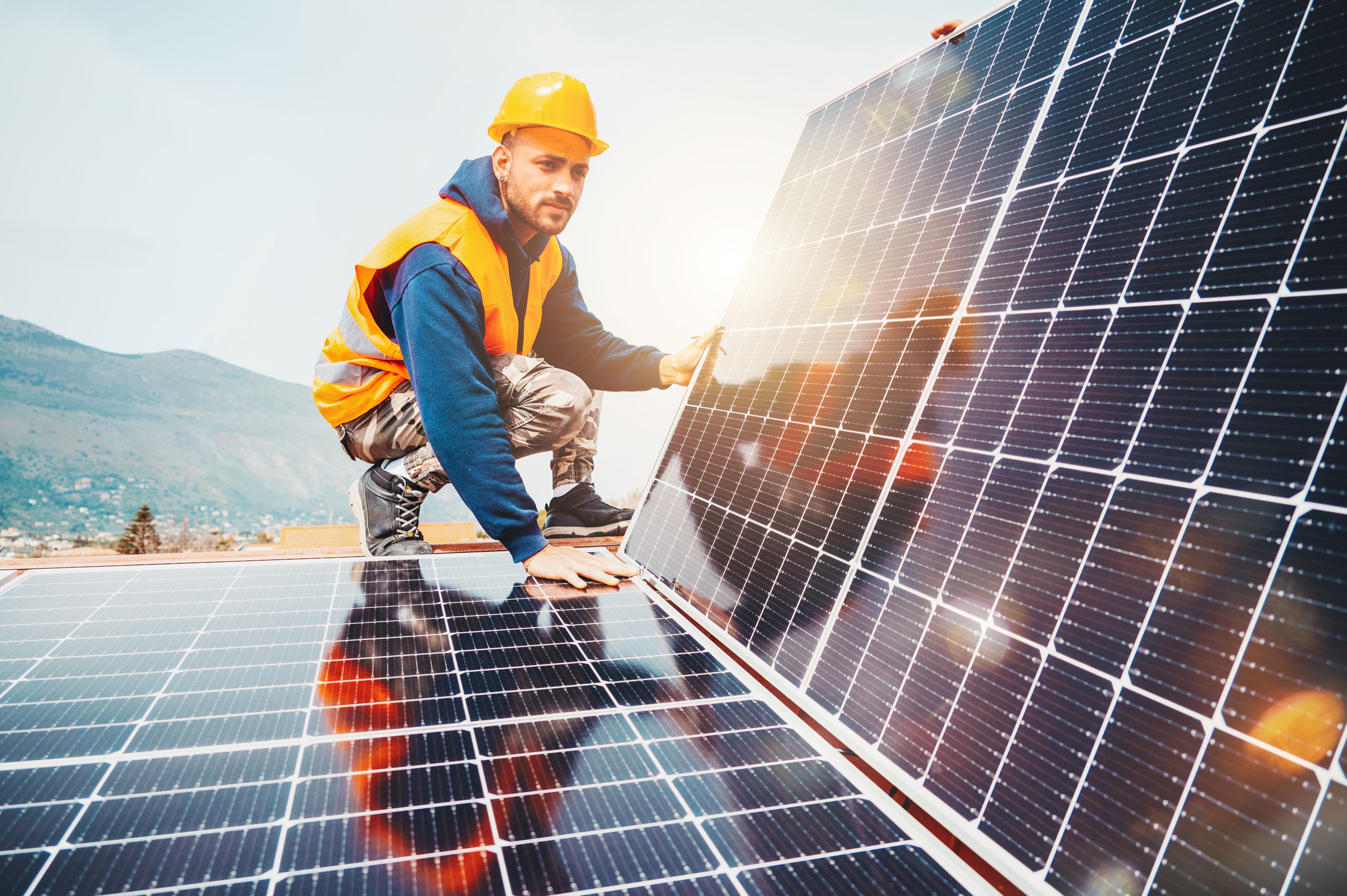

PV panels range in size from small solar kits and rooftop installations with a capacity of 3-20 kW to complex systems with a capacity of hundreds of megawatts.
Solar module prices have been falling continuously. For example, according to IRENA, prices have fallen to 93% between 2010 and 2020. In April 2024, it was recorded lowest price globally.
Solar heating and cooling (SHC) technologies collects heat energy from the sun and uses this heat to provide hot water for space heating and cooling in residential, commercial and industrial applications.
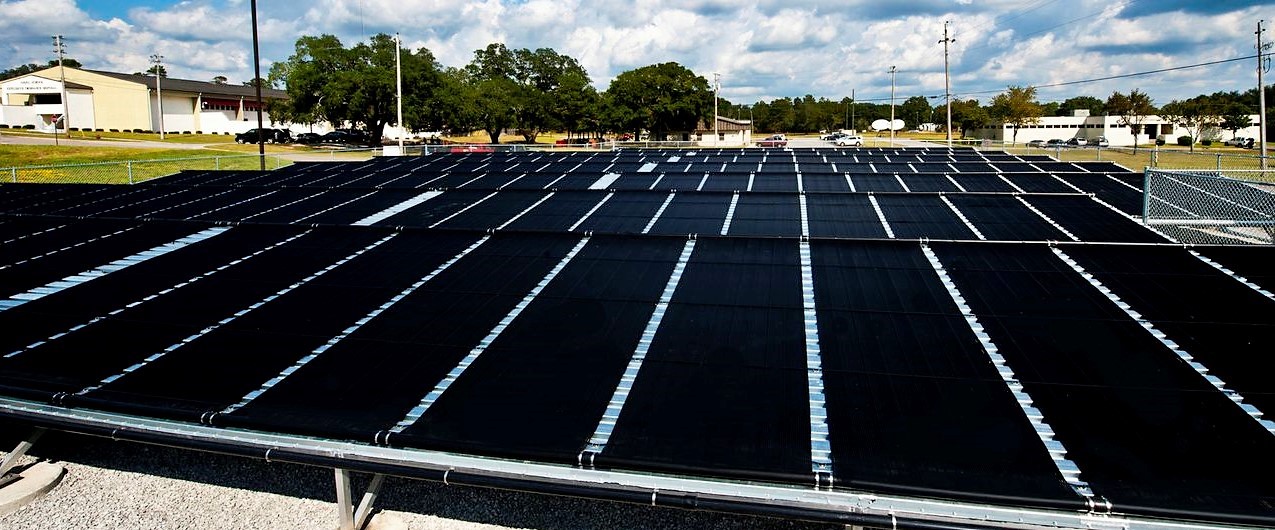

Photo source: SEIA
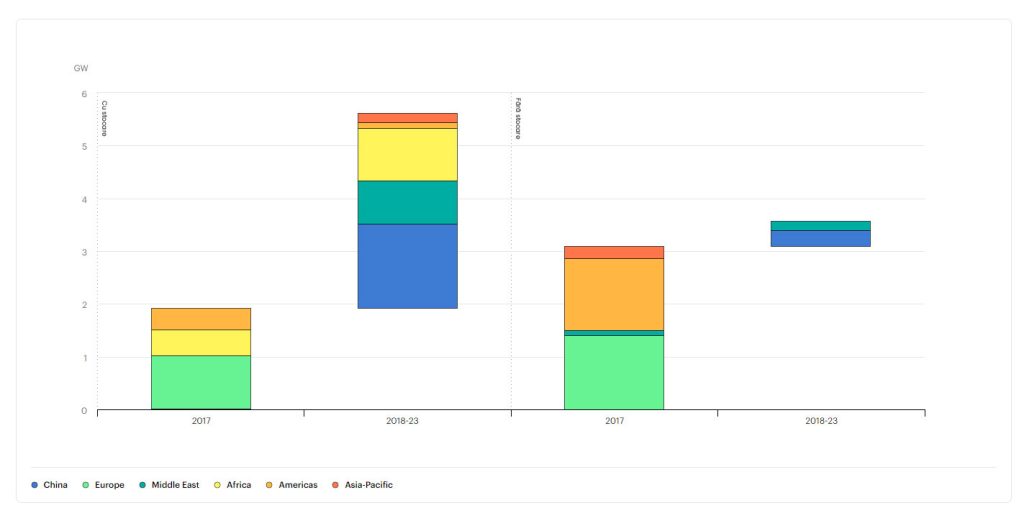
Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) uses mirrors to focus the sun's rays. These rays heat the working fluid, which creates steam to drive a turbine and generate electricity. CSP is used to generate electricity in large power plants. Global CSP installed capacity is growing, according to IEA.
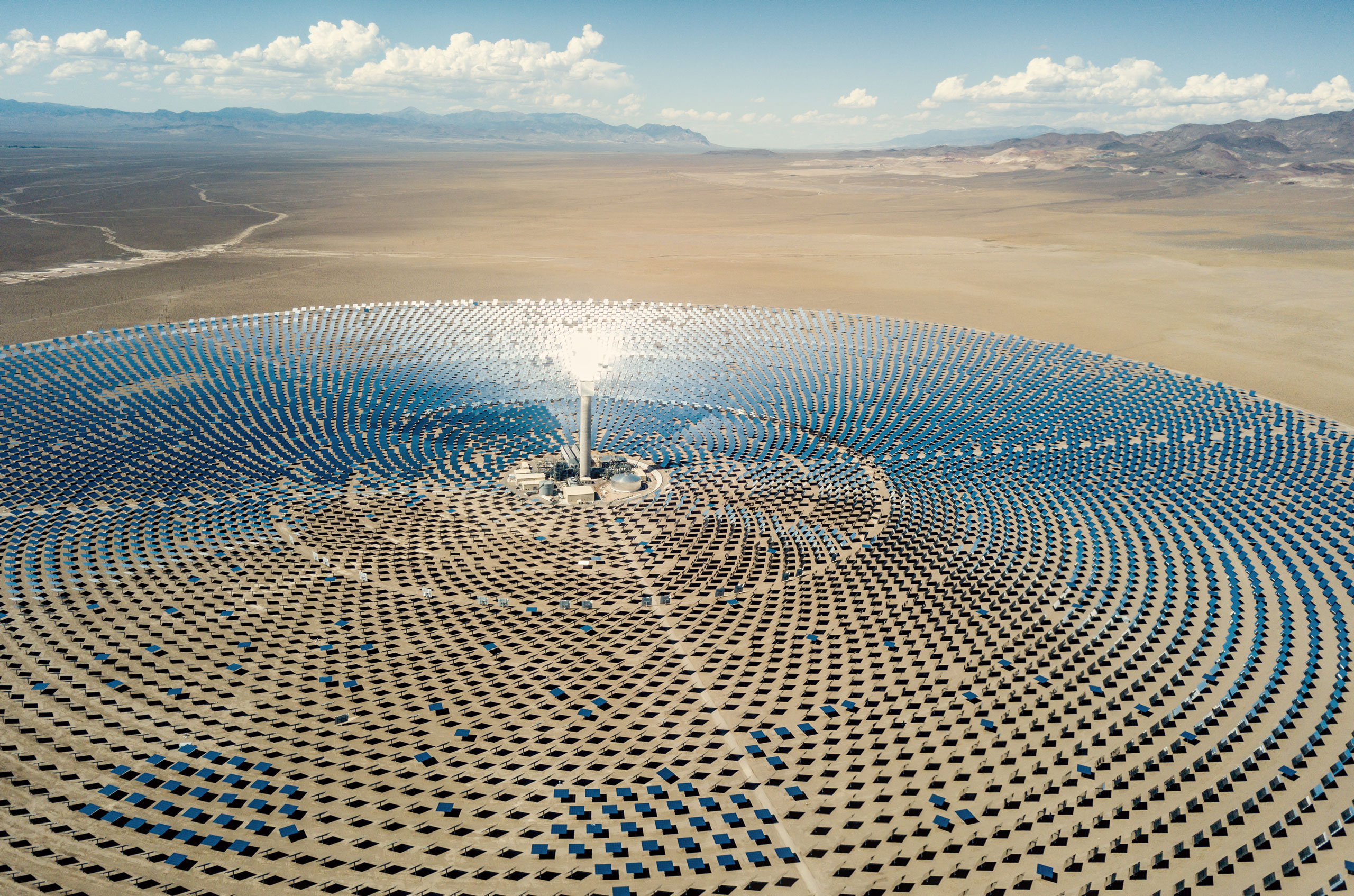

One of the main advantages of a CSP plant over a solar PV plant is that can be equipped with molten salts in which heat can be stored, allowing electricity generation during the night.
Global CSP capacity by technology, 2017 - 2023
Source: iea.org
2. How much solar energy does Romania produce?
According to INSIn Romania, solar energy produced in photovoltaic installations in the period January - November 2023 was 1602.3 million kWh, down by 120.1 million kWh compared to the corresponding period of 2022.
3. What are the major photovoltaic projects in Romania?
In Romania there are over 880 photovoltaic projects large-scale (with installed capacity greater than 5MW), with a cumulative capacity of approximately 46,600 MW.
Existing projects are concentrated in the southern and western parts of the country. Dolj (70) and Olt (56) counties are the leaders, followed by Prahova (51), Giurgiu (51), Bihor (50), Dâmbovița (46) and Teleorman (45). More information about large-scale PV projects in Romania can be found in the study by energynomics.ro.

4. How many consumers does Romania have?
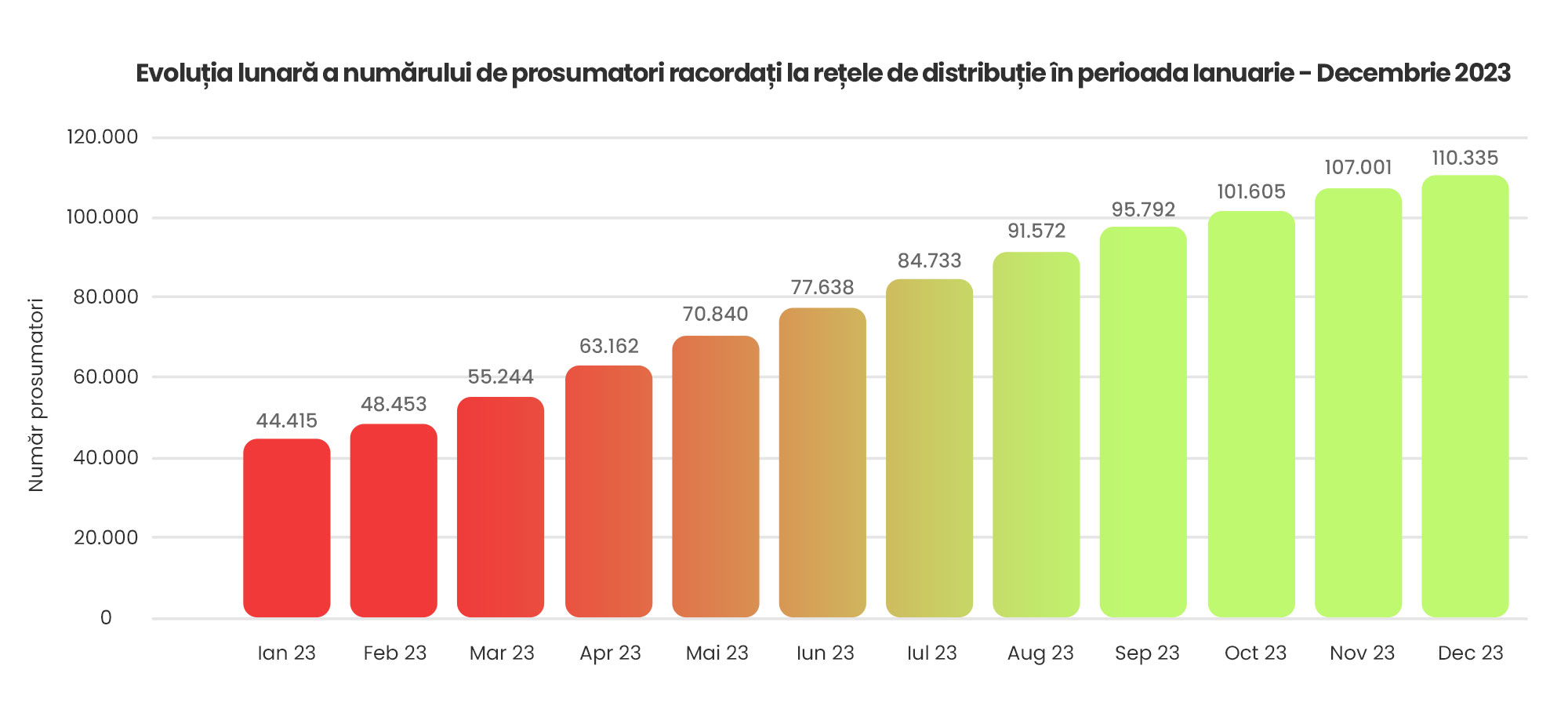
At the end of 2023, there were 110,355 prosumers in Romania, according to ANRE. The total installed capacity reached 1,442 MW, i.e. the cumulative power of the two nuclear reactors at Cernavodă. Last year, Romania saw a monthly increase in the number of prosumers, according to the same source.
Source: investenergy.ro
The favourable attitude of those who want to be prosumers could continue in 2024, especially after the Romanian state announced earlier this year, Disclaimer to the so-called "sun tax". The public debate was triggered by an emergency ordinance that would have allowed ANRE to charge prosumers from 1 December 2026, if their capacity would have exceeded 8% of the total power generation capacity in Romania.
5. How does the state encourage solar energy production?
In April 2024, the Ministry of Energy launched two new calls for projects to support the production and storage of renewable electricity (solar, wind and hydro).
The two funding schemes involve more than €800 million in funding:
-
- The first call has a 415 million budget, for the construction of renewable energy production plants for self-consumption with storage batteries.
- The second call aims to support investments in new renewable electricity generation capacity for projects concerning companies and autonomous companies. The total estimated budget is €400 million and represent non-repayable amounts from the Modernisation Fund.
Electricity storage means storing energy for later use. There are several technologies available for storing energy, for example batteries or hydrogen. This means that energy from solar or other sources can be used when there is no direct generation (e.g. at night and on cloudy days). Developing storage capacity is important for energy security, but also for the whole process of decarbonising the energy system by increasing the capacity to use renewable energy.
In December 2023, the Ministry of Energy launched a call for projects dedicated to increasing electricity storage capacity in Romania (batteries). The main objective is to have at least 240 MW of battery storage capacity in operation by 30 June 2026. The total budget is the equivalent in RON of €79,600,000 of European funds provided through the Recovery and Resilience Mechanism.
Sources:
https://www.seia.org/initiatives/about-solar-energy
https://www.irena.org/Energy-Transition/Technology/Solar-energy
https://www.seia.org/initiatives/solar-heating-cooling
https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/charts/csp-capacity-by-technology-2017-2023
https://insse.ro/cms/sites/default/files/com_presa/com_pdf/energie11r23.pdf
https://www.investenergy.ro/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Situatie-prosumatori-31.12.2023.pdf